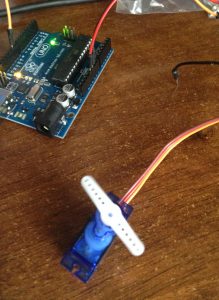
Il servomotore è un motorino con poca potenza. Nei kit in cui viene venduto è accoppiato a delle sbarre ed eliche di plastica, unitamente a delle viti per fissarlo. Il servomotore è in grado di muoversi con una rotazione fino a 180°.
Il collegamento è piuttosto semplice basta collegare ai vari cavi femmina, dei cavi maschi.
Lo schema è il seguente:
- il cavo marrone alla massa di Arduino,
- il rosso all’alimentazione 5V di Arduino,
- il cavo arancione al pin 9 (o altro a propria scelta).
Poi aprire il software Arduino andare su File – Esempi – Servo – Sweep e caricare il codice.
/* Sweep
by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com>
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
https://web.archive.org/web/20200728193139/https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Sweep
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
// in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable ‘pos’
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable ‘pos’
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
}




UN GRAZIE A TUTTI SPERANDO CHE I CANALI DTT SI VEDANO .
Come si riesce a capire se un tuo articolo è stato scelto ma non riconosciuto il compenso ?
Salve a tutti io sono in Italia e ho un conto banco posta ho associato al mio c/c un nuovo…
devo accettare il mifid posta x fare l isee dal sito
Dalla seconda in poi non mette il nome, ma mette il numero progressivo tra parentesi, poichè trova i link precedenti…